What’s the connection between genetics and inflammation in rare diseases?
What if the very system designed to protect your body was actually the one causing the damage? For many living with a rare disease can feel isolating. It often begins with a long, frustrating search for answers, a “diagnostic odyssey,” and leads to managing complex symptoms without a clear path forward. Today, we want to walk with you through understanding a common thread that weaves through many rare conditions: inflammation.
We’re going to take a deeper look at what inflammation is and how it impacts the body, especially in the context of rare diseases. We know that science can sometimes feel complex, but our goal is to break it down together.
What is Inflammation?
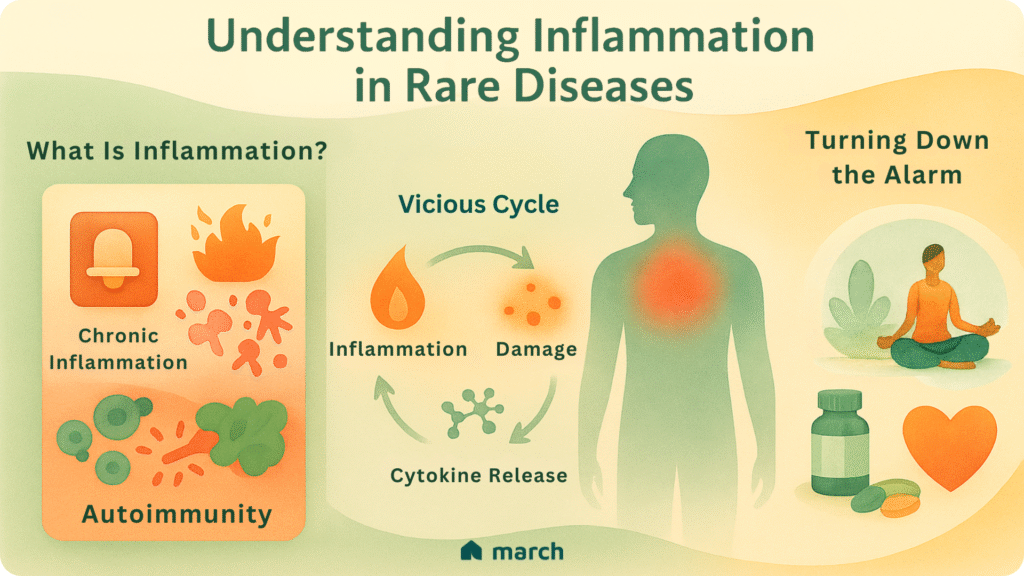
At its core, inflammation is your body’s natural immune response to something irritating, like an injury or an infection. Think of it like an internal fire alarm:
- Acute inflammation is a quick, short-lived response – the alarm rings, your body rushes to the scene (with redness, heat, swelling, and pain), deals with the problem, and then the alarm turns off. This is essential for healing.
- Chronic inflammation, however, is different. This is when the fire alarm gets stuck “on” for weeks, months, or even indefinitely. Instead of protecting you, this constant, low-level activation can actually start to harm healthy tissues.
Many rare diseases, especially those rooted in autoimmune or genetic issues, involve significant inflammatory components. This persistent “stuck alarm” can drive the progression of the disease and make managing symptoms incredibly challenging.
Inflammation’s Underlying Autoimmune Connection
A major reason for this issue in many rare diseases is a process called autoimmunity. Normally, your immune system is excellent at telling the difference between your own cells and foreign invaders like viruses or bacteria. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system gets confused and mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy cells and tissues. This friendly fire results in inflammation and tissue damage.
Many rare diseases are autoimmune in nature, which means the body’s own defense system is the cause of the ongoing inflammation. This is why managing inflammation is so crucial for these conditions.
The Root of the Challenge
One of the trickiest things about chronic inflammation is that it can happen “silently,” without obvious symptoms at first. Unlike a sprained ankle that screams with pain, chronic inflammation can quietly damage your body over time, breaking down healthy tissue in a misdirected attempt at repair. For those with rare diseases, this hidden progression can further delay accurate diagnosis and timely support.
At the heart of this constant signaling are substances called cytokines. These are like the body’s messengers, telling immune cells what to do. In chronic inflammation, the pro-inflammatory messengers become overactive, constantly signaling for cells to stay alert, leading to ongoing damage. This creates a “vicious cycle” where inflammation causes damage, and that damage, in turn, fuels more inflammation.
Managing the Inflammatory Journey
For years, managing inflammation often meant treating symptoms. But as our understanding grows, we recognize that addressing this underlying process is key. While there’s no single “quick fix,” however, a holistic approach combining medical therapies with powerful lifestyle changes can make a real difference.
This includes focusing on an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods and added sugars. Lifestyle shifts like regular exercise, effective stress management, and prioritizing good sleep are also incredibly important. These aren’t just about feeling better; they actively support your body’s ability to regulate its immune system and reduce inflammation. Medical therapies, including targeted drugs, also play a vital role in controlling and slowing disease progression.
Marching Forward: Hope, Realism, and the Road Ahead
While inflammation can cause lasting harm, we know that managing it well, especially early on, can truly change the course of a disease.
We’re here to support you with clear, trustworthy information. We’ll celebrate every breakthrough and be honest about the challenges that remain. Your journey matters, and we’re on this path of discovery together. You are not alone.
For a comprehensive look at this topic, tune into our podcast episode where we explore the subject in detail.
Sources
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. In brief: What is an inflammation? – InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279298/
- pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease – PMC – PubMed Central: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7919414/
- ucl.ac.uk. Department of Inflammation and Rare Diseases | Faculty of Medical Sciences – University College London: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/medical-sciences/divisions/medicine/departments/department-inflammation-and-rare-diseases
- my.clevelandclinic.org. What are Cytokines? Types & Function – Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24585-cytokines
- arthritis.or. Anti-Inflammatory Diet Do’s and Don’ts | Arthritis Foundation. https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/healthy-living/nutrition/anti-inflammatory/anti-inflammatory-diet
- pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Exercise Training – PMC. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4243532/
- springermedizin.de. Sleep and inflammation: a bidirectional relationship. https://www.springermedizin.de/sleep-and-inflammation-a-bidirectional-relationship/50565596
- elcaminohealth.org. The Causes and Effects of Inflammation | El Camino Health. https://www.elcaminohealth.org/stay-healthy/blog/anti-inflammatory-diet-foods-eat-and-avoid
- everydayhealth.com. The Link Between Stress and Inflammation – Everyday Health. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/in-depth/stress/art-20046037
